Introduction
Crystal technology has revolutionized the field of optics, lasers, and medical technology. Among the champions in this arena are Alexandrite and YAG (Yttrium Aluminum Garnet). Both these crystals have found their niches in various applications, but how do they stack up against each other? Let’s delve into an in-depth comparison.
Understanding Alexandrite: The Gem of Lasers
Origin and Characteristics
Alexandrite, a rare and precious gemstone, belongs to the chrysoberyl family. Its uniqueness lies in its remarkable ability to change color under varying lighting conditions, shifting from green in daylight to red under incandescent light. This optical phenomenon, known as the “alexandrite effect,” has captivated gem enthusiasts for centuries.
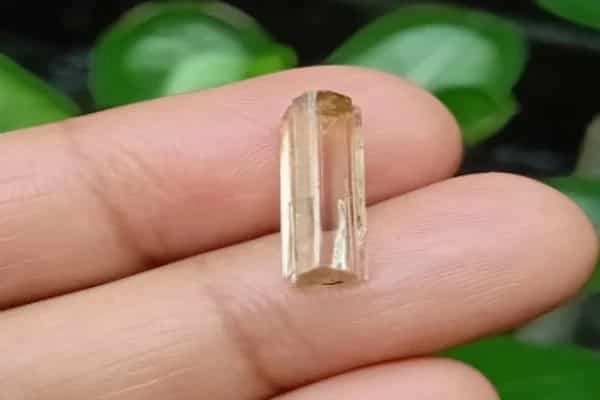

In the world of lasers, alexandrite serves as the basis for a highly specialized type of laser, emitting a distinct red beam with a wavelength of approximately 755 nanometers (nm). This specific wavelength is key to its utility in various laser applications.
Key Applications
Hair Removal: Alexandrite lasers have gained widespread recognition for their exceptional effectiveness in hair removal treatments. These lasers are particularly well-suited for this purpose because they target melanin, the pigment responsible for hair color. This targeting mechanism makes alexandrite lasers versatile, allowing them to be used on individuals with a broader range of skin tones compared to some other laser types.
Vascular Lesions: The deep penetration of alexandrite lasers into tissues, coupled with their selective absorption by hemoglobin, makes them a valuable tool for treating vascular lesions. Conditions like spider veins and port-wine stains respond well to this form of laser therapy.
Tattoo Removal: The versatility of alexandrite lasers extends to tattoo removal. Their ability to target a wide spectrum of pigments, including dark and multi-colored tattoos, has made them a popular choice among individuals seeking tattoo removal procedures.
Advantages
Speed: Alexandrite lasers are known for their speed and efficiency in delivering treatments. Their high repetition rate enables them to cover larger treatment areas in a shorter amount of time. This is particularly advantageous in procedures like hair removal, where efficiency and patient comfort are essential.

Versatility: The versatility of alexandrite lasers is a significant asset. Their capacity to target different pigments, including melanin and various tattoo ink colors, makes them valuable tools in both medical and cosmetic treatments. Whether it’s achieving smoother, hair-free skin or addressing vascular lesions and unwanted tattoos, alexandrite lasers offer versatility and effective results.
In conclusion, alexandrite lasers, with their origins in the captivating gemstone world, have found a unique and essential role in laser technology. Their ability to emit a red beam with specific characteristics makes them invaluable in a variety of applications, from hair removal to the treatment of vascular lesions and tattoo removal. With advantages like speed and versatility, alexandrite lasers continue to be a favored choice in the field of laser-based medical and cosmetic treatments.
Diving Deep into YAG: The All-Rounder Crystal
Origin and Features
Yttrium Aluminum Garnet (YAG) is a synthetic crystal that has found its niche in the realm of laser technology. This versatile crystal, often doped with rare earth elements like neodymium (Nd:YAG), possesses unique properties that make it invaluable for various laser applications.

Principal Uses
Cataract Surgery: One of the primary applications of YAG lasers is in the field of ophthalmology. After cataract surgery, a common complication called posterior capsular opacification can occur, leading to cloudy vision. Nd:YAG lasers are used to create a small opening in the cloudy posterior capsule, restoring clear vision. This procedure is minimally invasive and highly effective.
Glaucoma Treatment: YAG lasers play a crucial role in glaucoma management. They are used to create a tiny drainage hole in the eye’s trabecular meshwork, facilitating the outflow of aqueous humor. By doing so, these lasers help alleviate intraocular pressure, which is a significant factor in glaucoma development. The procedure is known as selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT).
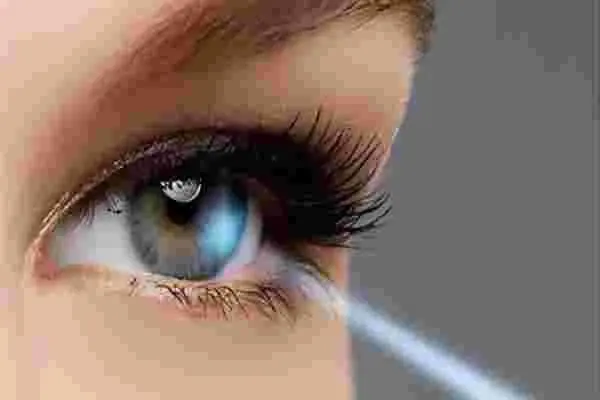

Skin Resurfacing: YAG lasers are also employed in the field of dermatology for skin resurfacing and rejuvenation. They are particularly effective in addressing skin issues such as wrinkles, acne scars, and sun damage. YAG lasers work by stimulating collagen production and removing damaged skin layers, resulting in improved skin texture and appearance.
Strengths
Deep Penetration: One of the standout features of YAG lasers is their ability to penetrate deep into tissues. This deep penetration is particularly advantageous in treatments like glaucoma, where precise targeting of deeper structures is necessary. YAG lasers can effectively reach these structures without causing damage to the surrounding tissues.
Safety: YAG lasers are considered safe for various medical and ophthalmic procedures, especially those involving the eye. Their precision and minimal invasiveness make them a preferred choice for eye surgeries, where utmost accuracy is paramount to preserve vision.
In conclusion, YAG, specifically Nd:YAG, is a synthetic crystal that has proven to be an all-rounder in laser technology. Its applications range from addressing post-cataract surgery complications to managing glaucoma and providing effective skin resurfacing treatments. Its ability to penetrate deep tissues and maintain safety in delicate procedures underscores its significance in the world of medical and cosmetic laser applications.
Alexandrite vs. YAG: The Face-Off
When comparing Alexandrite and YAG crystals for laser applications, it’s essential to recognize that each has its distinct strengths and characteristics. Let’s delve deeper into the key differences between these two crystals:
Wavelength and Penetration:
Alexandrite lasers typically operate at a wavelength of 755 nm, which makes them well-suited for procedures that target melanin in the skin. The 755 nm wavelength is particularly effective for hair removal and treating pigmented lesions, such as age spots and freckles. In contrast, Nd:YAG lasers operate at a longer wavelength of 1064 nm, allowing them to penetrate deeper into the skin. This deeper penetration is advantageous for applications like tattoo removal, where the ink is located in the deeper layers of the skin. However, the longer wavelength also means that Nd:YAG lasers have less melanin absorption, making them a safer option for individuals with darker skin tones.
Skin Types:
One of the critical distinctions between Alexandrite and YAG lasers is their suitability for different skin types. Alexandrite lasers are known for their versatility and can effectively treat a wide range of skin tones. However, they may not be the ideal choice for individuals with very dark skin because the high melanin absorption could lead to complications like hyperpigmentation. In such cases, Nd:YAG lasers are often preferred, as they are less likely to cause pigmentation issues on dark skin.
Treatment Duration:
The repetition rate of laser procedures can significantly impact treatment duration. Alexandrite lasers typically have a faster repetition rate, making procedures quicker and more time-efficient. This is particularly advantageous for cosmetic treatments like hair removal, where speed is a priority.
Versatility in Application:
While both Alexandrite and YAG lasers are versatile and have a wide range of applications, their primary areas of focus differ. Alexandrite lasers are prominently used in cosmetic procedures, such as hair removal, skin rejuvenation, and the removal of pigmented lesions. On the other hand, Nd:YAG lasers have found extensive use in the medical field, especially in ophthalmology for treating eye conditions like glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy. They are also highly effective in tattoo removal and non-ablative skin tightening.
Concluding Insights: Choosing the Right Crystal
The choice between Alexandrite and YAG lasers should not be framed as determining which crystal is universally superior. Instead, it hinges on understanding the specific requirements of the procedure at hand. Alexandrite lasers excel in cosmetic applications, offering fast and effective solutions for a wide range of skin types. Meanwhile, Nd:YAG lasers are valued for their ability to penetrate deeper into tissues, making them indispensable in medical and specialized applications. Ultimately, the “better” crystal is the one that aligns perfectly with the task at hand, ensuring optimal results and patient safety.
FAQs
- 1.Is Alexandrite safe for all skin types?
While it’s suitable for a wider range of skin tones, utmost care should be taken with very dark skin types. Consultation with professionals is advised. - 2.Are there any side effects to YAG laser treatments?
While YAG lasers are generally safe, potential side effects include redness, swelling, and in rare cases, scarring or discoloration. - 3.Can Alexandrite lasers treat deep-set tattoos?
Yes, but it might require more sessions compared to superficial tattoos. The laser’s effectiveness also depends on the tattoo’s pigment colors. - 4.How many sessions are typically required for hair removal using Alexandrite?
Usually, 6-8 sessions are recommended, but it varies based on individual factors like hair density and growth cycle. - 5.Are YAG lasers used in cosmetic treatments?
Yes, besides medical applications, they are employed in skin resurfacing, addressing wrinkles, scars, and other skin issues.

Frank
Frank graduated from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, majoring in optics. As a technical engineer at Crylink Company, he deeply understands crystal materials and laser components.
Related Video(s) with this Article
Related Product(s) with this Article
Related Application(s) with this Article
