Cr:ZnSe

Cr: ZnSe laser crystal has the following advantages:
- Normally no excited state absorption
- Upper-level conversion
- An extremely broad absorption band
- Large emission cross-section
It has superb fluorescence quantum efficiency at room temperature extra broad emission width as well as good chemical and mechanical properties, which make it become an excellent source of efficient and powerful tunable mid-infrared laser. Because of mid-infrared wavelength band is the window of atmosphere, the Cr: ZnSe laser crystal has important application prospect in the field of photo-communication, pollution gas detection, industrial combustion product test and so on.
Features of Cr: ZnSe Laser Crystal:
- Broad tunability (lasing from 2.1-3.1 μm)
- Broad absorption bands
- Large gain cross-section (σemission ~ 9 × 10-19 cm2)
- Minimal problem of excited state absorption (no spin-allowed excited state transitions from the upper laser level)
- High thermal conductivity − better than YAG (18 W/m·K in ZnSe versus 13 W/m·K in YAG)
- High IR (0.6-20 μm) transparency
Material Specifications
| Crystal Structure | Cubic |
| Poisson Ratio | 0.28 |
| Thickness/Diameter Tolerance | ±0.05mm |
| Orientation Tolerance | < 0.5° |
| Flatness | <λ/8@632nm |
| Wavefront Distortion | <λ/4@632nm |
| Surface Finish | 10-5(MIL-O-13830A) |
| Parallelism | 30” |
| Perpendicularity | 15ˊ |
| Clear Aperture | >90% |
| Chamfer | <0.2×45° |
| Melting Point | 1520 ºC |
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Thermal Expansion Coeff. @20ºC | 1.5×10-6/ºC |
| Thermal Conductivity Coeff. @20ºC | 14 W/m/ºK |
| Specific Heat | 0.79 J/g K |
| Density | 5.27 g/cm³ |
| Durability Knoop Hardness | 112 kgf/mm² |
| Mohs Hardness | 8.5 |
| Young's Modulus | 67 GPa |
| Modulus of Rupture | 55 MPa |
| Orientation | <111>or <100> |
Optical and Spectral Properties
| Laser Wavelength | 2150 – 2600 nm |
| Emission Linewidth | <1 nm |
| Emission Linewidth | 9×10-19 cm² |
| Intrinsic Loss @1064nm | <0.003 cm-1 |
| Refractive Index (n) @ 1650nm | 2.455 |
| Thermal Optical Coeff. (dn/dT) @nm | 61×10-6/ºC |
Absorption and Emission Spectra
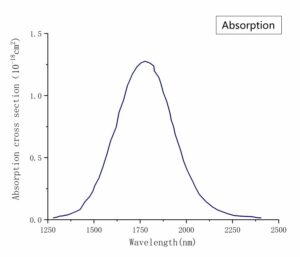 | 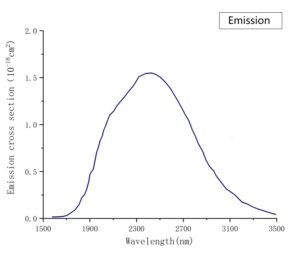 |
References
| [1] Dai T Y , Xu X G , Li X L , et al. 41kHz repetition rate passively Q-switched Ho:YAP laser with Cr:ZnS as a saturable absorber[J]. Optik – International Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2016:4844-4847. |
| [2] Dai Y , Li Y , Zou X , et al. Compact passively Q-switched Tm:YLF laser with a polycrystalline Cr:ZnS saturable absorber[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2014, 57:202-205. |
| [3] Hoemmerich U , Jones I K , Nyein E E , et al. Comparison of the optical properties of diffusion-doped polycrystalline Cr:ZnSe and Cr:CdTe windows[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2006, 287(2):450-453. |
| [4] Alphan, Sennaroglu, and, et al. Concentration dependence of fluorescence and lasing efficiency in Cr2+:ZnSe lasers[J]. Optical Materials, 2007. |
| [5] Tablero C . Impurity–host interactions in Cr-substituted ZnSe[J]. Solid State Communications, 2007, 143(8-9):399-402. |
| [6] Kim C , Martyshkin D V , Fedorov V V , et al. Middle-infrared random lasing of Cr 2+ doped ZnSe, ZnS, CdSe powders, powders imbedded in polymer liquid solutions, and polymer films[J]. Optics Communications, 2009, 282(10):2049-2052. |
| [7] Fedorov V V , Konak T , Dashdorj J , et al. Optical and EPR spectroscopy of Zn:Cr:ZnSe and Zn:Fe:ZnSe crystals[J]. Optical Materials, 2014, 37:262-266. |
| [8] Qamar F Z , King T A . Passive Q-switching of the Tm-silica fibre laser near 2 μm by a Cr 2+:ZnSe saturable absorber crystal[J]. Optics Communications, 2005, 248(4-6):501-508. |
| [9] Wang X Y , Chen Z , Zhang L , et al. Preparation, spectroscopic characterization and energy transfer investigation of iron-chromium diffusion co-doped ZnSe for mid-IR laser applications[J]. Optical Materials, 2016, 54:234-237. |
| [10] A.V Podlipensky and V.G Shcherbitsky and N.V Kuleshov and V.P Mikhailov and V.I Levchenko and V.N Yakimovich and L.I Postnova and V.I Konstantinov. Pulsed laser operation of diffusion-doped Cr2+:ZnSe[J]. Optics Communications, 1999. |
| [11] Min, Chen, Hongmei, et al. Reparative effect of diffusion process on host defects in Cr2+ doped ZnS/ZnSe[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2014. |
| [12] S Kück. Spectroscopy and laser characteristics of Cr 2+-doped chalcogenide crystals — overview and recent results[J]. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2002, 341(1-2):28-33. |
| [13] Demirbas U , Sennaroglu A , Somer M . Synthesis and characterization of diffusion-doped Cr2+:ZnSe and Fe2+:ZnSe[J]. Optical Materials, 2006, 28(3):231-240. |
If you are intereted in Cr:ZnSe, please click the button below to enquire or ask for a samplel.
Related article(s) with Cr:ZnSe:
Related case study with Cr:ZnSe:
Related solution(s) with Cr:ZnSe:
There is no related application(s) with this product, please visit solutionspage to find out more.
Related video(s) with Cr:ZnSe:
There is no related video(s), please visit videos page to find out more.
