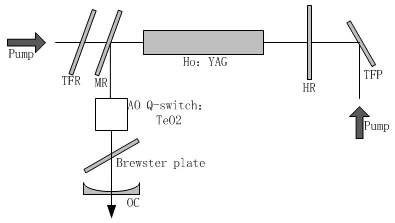
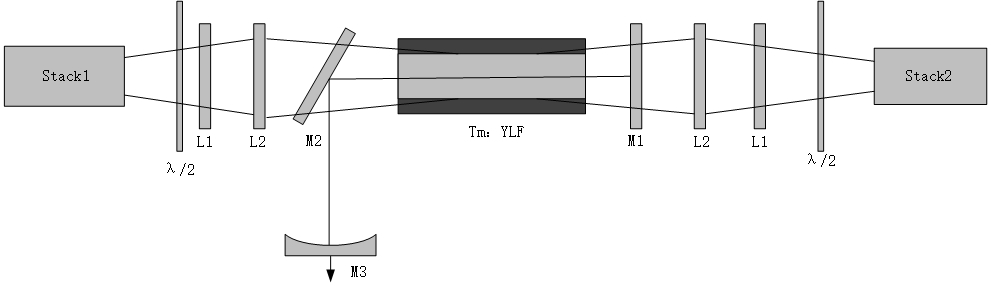
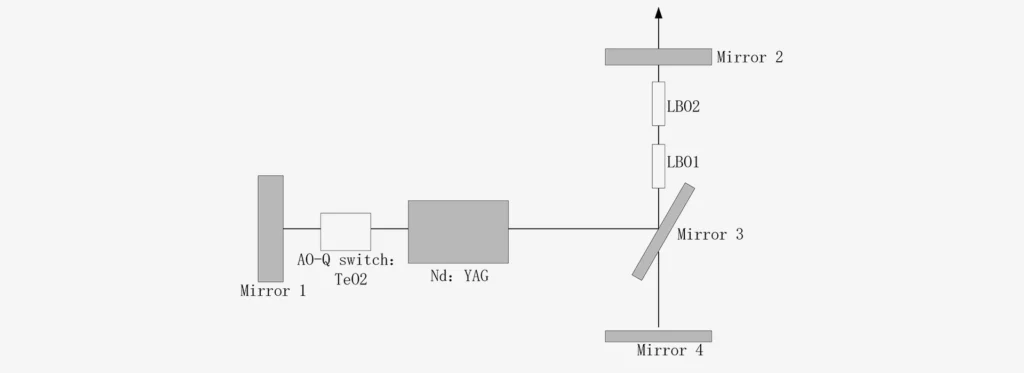
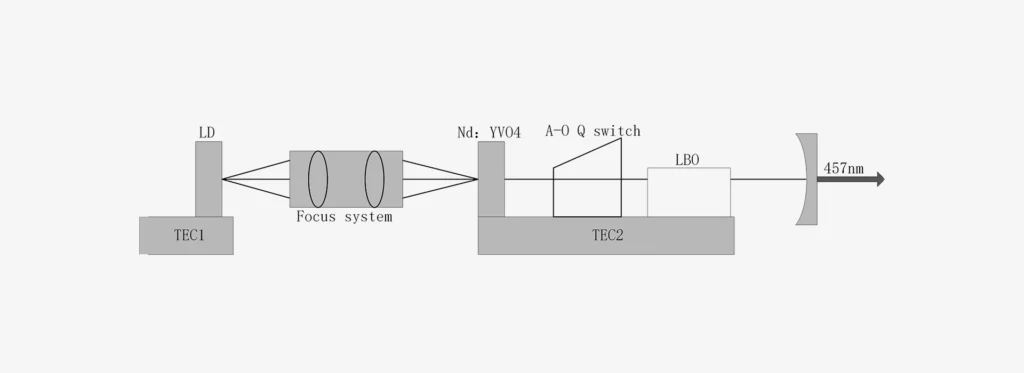
TeO2 Crystal

TeO2 crystal, also known as tellurium dioxide, is a kind of acousto-optic crystal material with high-quality factors and excellent performance.
TeO2 crystal has the advantages of fast response, low driving power, and high diffraction efficiency, stable and reliable performance. It is widely used in various types of acousto-optic devices, such as:
- Acousto-optic deflectors
- Acousto-optic modulators
- Acousto-optic harmonizers
- Acousto-optic filters
- Tunable filters
Therefore, TeO2 crystals are a promising material for acousto-optic devices, especially for acousto-optic modulators and acousto-optic harmonizers. They have a wide range of applications in optical computing, optical communication, and optical microscopic imaging.
Features of TeO2 Crystal:
- High refractive index
- Low sound attenuation
- High Quality Factor
- High transparency to visible light
- Excellent sound and light characteristics
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Attribute | Numerical |
| Chemical Formula | TeO2 |
| Molar Mass | 159.60 g/mol |
| Color | Colorless, |
| Density | 5.99 ± 0.03 /cm3 |
| Melting Point | 733°C |
| Hardness | 3-4 Mohs Hardness Tester |
| Thermal Expansion | 10-6 К-1: α11= 17.7; α22 = 17.7; α33= 5.5 |
| Symmetry | Tetragonal Crystal System, 422 (D4) |
| Lattice Constant | a = 4.8122 Å; c = 7.6157 Å |
| Transmittance | >70% @ 633nm |
| Launch Range | 0.33 ~ 5.0 μm |
| Dielectric Constant | ε11 = 22.9; ε33 = 24.7 |
| Elastic Constants·10-10 N/m2 | c11 = 5.57; c33 = 10.58; c44 = 2.65; c66 = 6.59; c12 = 5.12; c13 = 2.18 |
| Photoelastic Coefficient@0.6328 μm | p11 = 0.0074; p12 = 0.187; p13 = 0.340; p31 = 0.0905; p33 = 0.240; p44 = -0.17; p66 = -0.0463 |
Refractive Index
| λ, μm | no | ne | Δn = ne– no |
| 0.4047 | 2.4315 | 2.6167 | 0.1852 |
| 0.4358 | 2.3834 | 2.5583 | 0.1749 |
| 0.4678 | 2.3478 | 2.5164 | 0.1686 |
| 0.48 | 2.3366 | 2.5036 | 0.167 |
| 0.5086 | 2.315 | 2.4779 | 0.1629 |
| 0.5461 | 2.2931 | 2.452 | 0.1589 |
| 0.5893 | 2.2738 | 2.4295 | 0.1557 |
| 0.6328 | 2.2597 | 2.4119 | 0.1522 |
| 0.6438 | 2.2562 | 2.4086 | 0.1524 |
| 0.69 | 2.245 | 2.3955 | 0.1505 |
| 0.8 | 2.226 | 2.373 | 0.147 |
| 1 | 2.208 | 2.352 | 0.144 |
Optical Activity, Along [001]
| λ, μm | p, deg/mm | λ, μm | p, deg/mm |
| 0.3698 | 587.1 | 0.5893 | 104.9 |
| 0.3783 | 520.6 | 0.6328 | 86.9 |
| 0.3917 | 437.4 | 0.7 | 67.4 |
| 0.4152 | 337.6 | 0.8 | 48.5 |
| 0.4382 | 271 | 0.9 | 37.4 |
| 0.463 | 221.1 | 1 | 29.5 |
| 0.4995 | 171.2 | 1.1 | 23.8 |
| 0.53 | 143.4 |
Acousto-optic Properties: λ=0.6328μm
| Nsound | Usound | Vsound 103 м/с | Nlight | Elight | M1 10-7сm2 · с/г | M210-18с3/г |
| [100] | [100] | 2.98 | [010] | [100] | 0.097 | 0.048 |
| [100] | [100] | – | [010] | [001] | 22.9 | 10.6 |
| [001] | [001] | 4.26 | [010] | [100] | 142 | 34.5 |
| [001] | [001] | – | [010] | [001] | 113 | 25.6 |
| [100] | [010] | 3.04 | [001] | optional | 3.7 | 1.76 |
| [110] | [110] | 4.21 | [-110] | [110] | 323 | 0.802 |
| [110] | [110] | – | [-110] | [001] | 16.2 | 3.77 |
| [101] | [101] | 3.64 | [-101] | [010] | 101 | 33.4 |
| [010] | [010] | 2.98 | [-101] | [101] | 42.6 | 20.4 |
| [110] | [-110] | 0.617 | [001] | optional | 68.6 | 793 |
| [101] | [-101] | 2.08 | [010] | [100] | 76.4 | 77 |
TeO2 Modulator Characteristics
| Main Features of АОM | TeO2Typical Values for Modulators |
| Optical Wavelength Range | 514nm, 633nm, 1064nm, 1330nm |
| Optical Aperture | 0.3 mm – 3 mm |
| Working Mode | Longitudinal, axis(001) |
| Light Rise Time | The beam diameter is 9-200 nsec |
| Beam Separation(633 nm) | 10-30 mrad |
| Diffraction Efficiency | 70-85 % |
| Modulation Frequency(-3db) | 6-50 MHz |
TeO2 Deflector Characteristics
| Main Features of АОD | TeO2Typical Values of Deflectors |
| Optical Wavelength Range | 540nm-530nm, 630nm-850nm, 700nm-1100nm, 1064nm, 1330nm |
| Optical Aperture | 1 mm – 10 mm |
| Working Mode | Shear wave, axis 3-15 degrees(110) |
| Center Frequency | 20- 200 MHz |
| Bandwidth | 20-100 MHz |
| Diffraction Efficiency | 60-95% |
| Time Aperture | 1-15 μs |
| Resolution(T.BW products) | 200-2000 |
| Light Rise Time | The beam diameter is 9-200 nsec |
| Angle | 10-100 mrad |
| ΔDeflection Angle | 5-50 mrad |
| RF input power | 0,1- 2 Wt |
TeO2 Tunable Filter Characteristics
| The Main Characteristics of a Spectacle OTF | TeO2 Typical value of AOTF |
| Tuning Range | 450-750nm, 900-1200nm, 1200-2500nm, 2500-5000nm |
| Bandwidth | 0.5 nm – 15 nm |
| Working Mode | Slow shear, non-collinear propagation |
| Corner Hole | 2-10 |
| Optical Aperture | 3×3 mm – 30×30 mm |
| Diffraction Efficiency | 70-85 % |
| RF Power | 1-10 Wt |
Spectrum
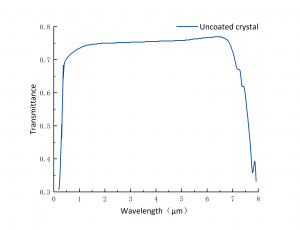 |
References
| [1] Mirzaei A , Park S , Sun G J , et al. CO gas sensing properties of In4Sn3O12 and TeO2 composite nanoparticle sensors[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 305(Mar.15):130-138. |
| [2] Dafinei I , Diemoz M , Longo E , et al. Growth of pure and doped TeO2 crystals for scintillating bolometers[J]. Nuclear Inst & Methods in Physics Research A, 2005, 554(1-3):195-200. |
| [3] Kokh A E , Shevchenko V S , Vlezko V A , et al. Growth of TeO2 single crystals by the low temperature gradient Czochralski method with nonuniform heating[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2013, 384(dec.1):1-4. |
| [4] S, Kumaragurubaran, and, et al. Investigations on the growth of Bi2TeO5 and TeO2 crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1999. |
| [5] Beke S , Kobayashi T , Sugioka K , et al. Time-of-flight mass spectroscopy of femtosecond and nanosecond laser ablated TeO2 crystals[J]. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2011, 299(1):5-8. |
| [6] Casali N , Bellini F , Dafinei I , et al. Monte Carlo simulation of the Cherenkov radiation emitted by TeO2 crystal when crossed by cosmic muons[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A Accelerators Spectrometers Detectors and Associated Equipment, 2013, 732(dec.21):338-341. |
| [7] Jalilian, Jaafar, Naseri, et al. Electronic and optical properties of paratellurite TeO2 under pressure: A first-principles calculation[J]. Journal for Light & Electronoptic, 2017. |
| [8] Syrbu N N , Cre?U R V . The superposition of one- and two-phonon absorption and radiation in TeO2 crystal[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 1996, 37(7):769–775. |
| [9] Mangin J , Veber P . PtTe2: Potential new material for the growth of defect-free TeO2 single crystals[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310(12):3077-3083. |
| [10] Sudha A , Maity T K , Sharma S L , et al. An extensive study on the structural evolution and gamma radiation stability of TeO 2 thin films[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2018, 74:347-351. |
| [11] A, Watterich, and, et al. Paramagnetic and diamagnetic defects in e− and UV-irradiated TeO2 single crystal[J]. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research, 2002. |
| [12] B C A A , B C B A , D A B C , et al. Production of high purity TeO 2 single crystals for the study of neutrinoless double beta decay[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2010, 312( 20):2999-3008. |
| [13] High-stability acousto-optical devices using bulk acoustic waves in TeO2[J]. Electronics Letters, 2007, 14(17):535-536. |
| [14] Barucci M , Brofferio C , Giuliani A , et al. Measurement of Low Temperature Specific Heat of Crystalline TeO2 for the Optimization of Bolometric Detectors[J]. Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 2001, 123(5-6):303-314. |
| [15] Xun G , Shang X , D Zhang. Study on SAW characteristics of amorphous-TeO2/36°Y-X LiTaO3 structures. IEEE, 2009. |
| [16] Stavrakieva D , Ivanova Y , Pyrov J . On the composition of the crystal phases in the PbO TeO2 system[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 1988, 23(5):1871-1876. |
| [17] Yong J K , Choi S W , Kang S Y , et al. Enhancement of the benzene-sensing performance of Si nanowires through the incorporation of TeO2 heterointerfaces and Pd-sensitization[J]. Sensors and Actuators B Chemical, 2017, 244(jun.):1085-1097. |
| [18] Physical properties and structural studies of lithium borophosphate glasses containing TeO 2[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2019, 270:547-552. |
| [19] Nagarajan V , Chandiramouli R . DFT investigation of NH3 gas interactions on TeO2 nanostructures[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2016, 26( 2):129-138. |
| [20] Park S , An S , Ko H , et al. Enhancement of ethanol sensing of TeO2 nanorods by Ag functionalization[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2013, 13(3):576-580. |
If you are intereted in TeO2 Crystal, please click the button below to enquire or ask for a samplel.
Related article(s) with TeO2 Crystal:
There is no related article with this product, please visit our articles page to find out more.
Related case study with TeO2 Crystal:
Related solution(s) with TeO2 Crystal:
Related video(s) with TeO2 Crystal:
There is no related video(s), please visit videos page to find out more.